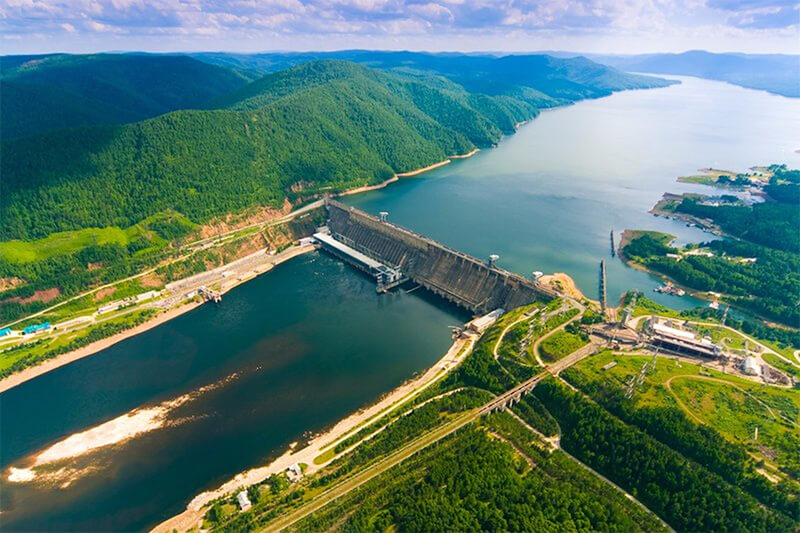
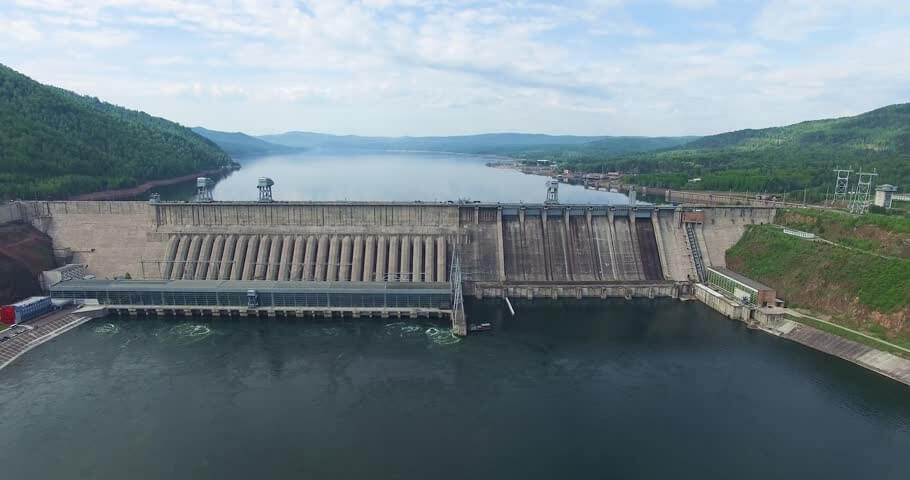
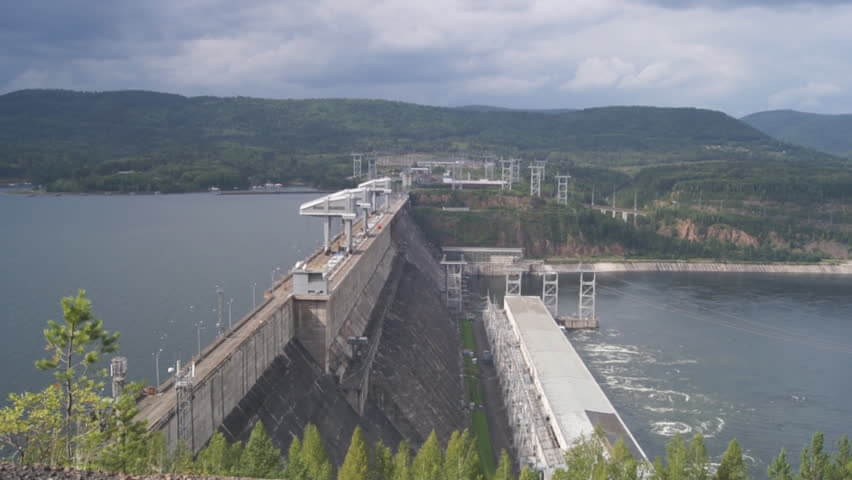
Krasnoyarsk Dam(Russian:Красноярская плотина) is a 124 meter (407 ft) high concrete gravity dam located on the Yenisey River about 30 kilometers (19 mi) upstream from Krasnoyarsk in Divnogorsk, Russia.
It was constructed from 1956 to 1972, and it supplies about 6,000 MW (six GW) of power, mostly used to supply the KrAZ (Krasnoyarsky Aluminievyy Zavod, the Krasnoyarsk Aluminum Plant).
Both power and aluminum plants are controlled by the RUSAL company.

Building parameters
The hydropower structure includes a 1065 m long and 124 m tall gravity concrete dam. Including the left dam (length 187.5 m), spillway dam (225 m), blind channel dam (60 m), power station dam (360 m) and right bank dam (232.5 m).
The dam construction capacity is 220 kV and 500 kV power receiving and distribution units.
The marine elevator has a pilot channel downstream.


5.7 million cubic meters of concrete were laid during the main construction of the dam.
The height of the upper pool is 243 m above sea level, the height of the lower pool is 141.7 to 152.5 m, the maximum discharge of the spillway during the flood is 14,000 cubic meters per second, and the total maximum flow of the water plant is 20600 cubic meters per second.
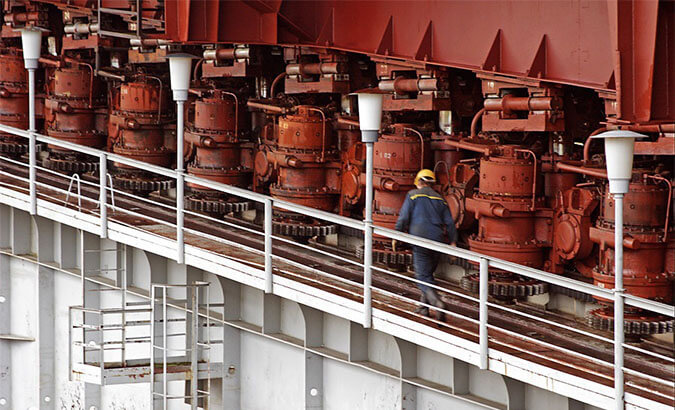
The hydropower building has 12 hydraulic units, each with a capacity of 500 MW and a design height of 93 m.
The turbine is located 139.5 m below sea level, the outer diameter of the impeller is 8.65 m, and the mass is 240 tons.
Krasnoyarsk Reservoir
As a result of the damming, the Krasnoyarsk Reservoir was created. This reservoir, informally known as the Krasnoyarsk Sea, has 2,000 square kilometers (770 sq mi) and a volume of 73.3 cubic kilometers (18 cu mi).
It is 388 km (241 mi) in length and 15 km (9 mi) in width at its widest, has an average depth of 36.6 m (120.1 ft), and a depth of 105 m (344 ft) near the dam.

Climate impact
The Krasnoyarsk Dam significantly influences the local climate.
Normally the river would freeze over in the bitterly cold Siberian winter, but because the dam releases unfrozen water year-round, the river never freezes in the 200 kilometers (120 mi) to 300 kilometers (190 mi) stretch of river immediately downstream from the dam.
In winter, the frigid air interacts with the warm river water to produce fog, which shrouds Krasnoyarsk and other downstream areas.

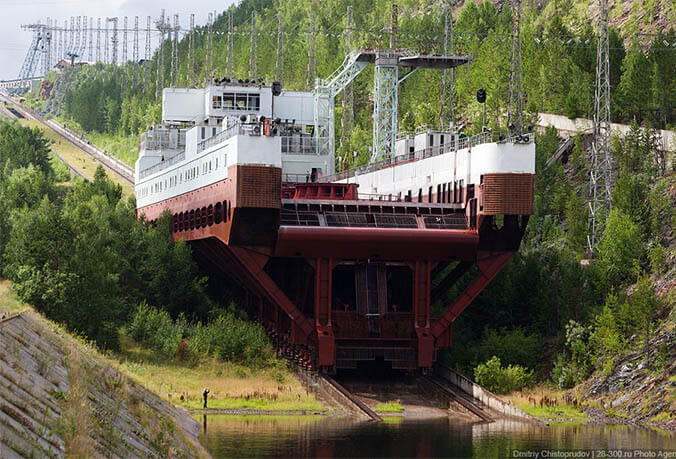
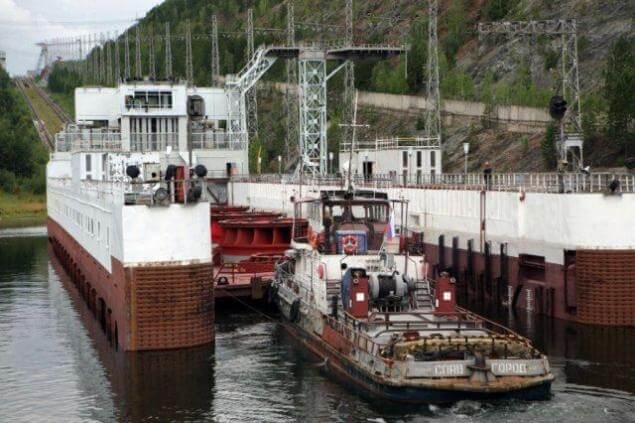
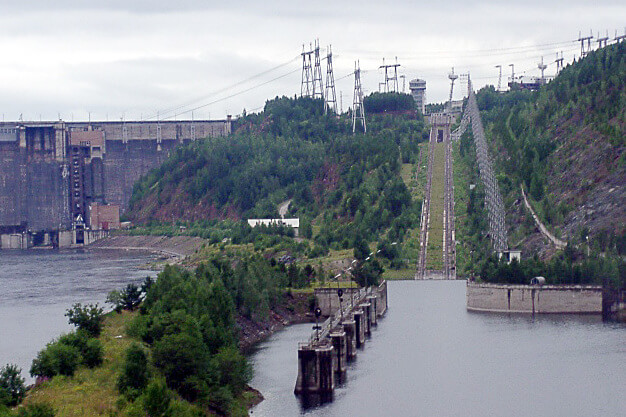
Ship lift
The dam is equipped with a canal inclined plane to allow passage of ships. In fact, It is an electric rack railway. The track gauge is 9,000 mm (29 ft 6 5⁄16 in), making it the widest-gauge railway of any type in the world.



At the time of its construction, this feat of modern engineering allowed ships to be physically moved in only 90 minutes.


10-ruble banknote
Krasnoyarsk Dam on the Russian 10-ruble banknote.
Beginning with the opening of the 10th turbine in April 1971, the powerhouse was the world’s single largest power plant until the Grand Coulee Dam in Washington State reached 6,181 MW in 1983.
The Krasnoyarsk Dam is a landmark symbol of Krasnoyarsk, and it is depicted on the 10-ruble banknote.

Krasnoyarsk Dam Data
- Country
- Russia
- Official name
- Красноярская плотина
- Location
- Divnogorsk, Russia
- Operator(s)
- RUSAL
- Status
- In use
- Type of dam
- Gravity dam
- Began
- 1956
- Opening date
- 1972
- Height
- 124 m (407 ft)
- Length
- 1,065 m (3,494 ft)
- Installed capacity
- 6,000 MW
- River
- Yenisey River
- Reservoi name
- Krasnoyarsk Reservoir
- Total capacity
- 73.3 km³ (17.6 cu mi)
- Reservoir area
- 2,000 km² (772 sq mi)
View Krasnoyarsk Dam on Google Satellite Map
Google satellite maps allow you to see building details more clearly, including natural landscapes such as mountains, rivers, deserts, sea and man-made engineering buildings.
If you are very interested in this engineering building, it is a good idea to click below Google Map icon. We will help you jump to the corresponding location of this building or engineering on Google satellite map.





























































so the ship is also controlled bu RUSAL?